The development status of special engineering plastics in China
Special engineering plastics refer to a type of engineering plastics with relatively high comprehensive performance and a long-term service temperature above 150°C. Internationally, the development of special engineering plastics originated in the late 1960s. From polyimide which came out in the 1960s to polyetheretherketone in the early 1980s, major companies in Europe, America and other countries have carried out a great deal of research and development on special engineering plastics. At present, more than ten varieties with application value and realized industrialization have been formed, which are widely used in technical industries such as electronics, automobiles, aerospace, and precision instruments.
Some Special Engineering Plastics Production Enterprises and Import Situations
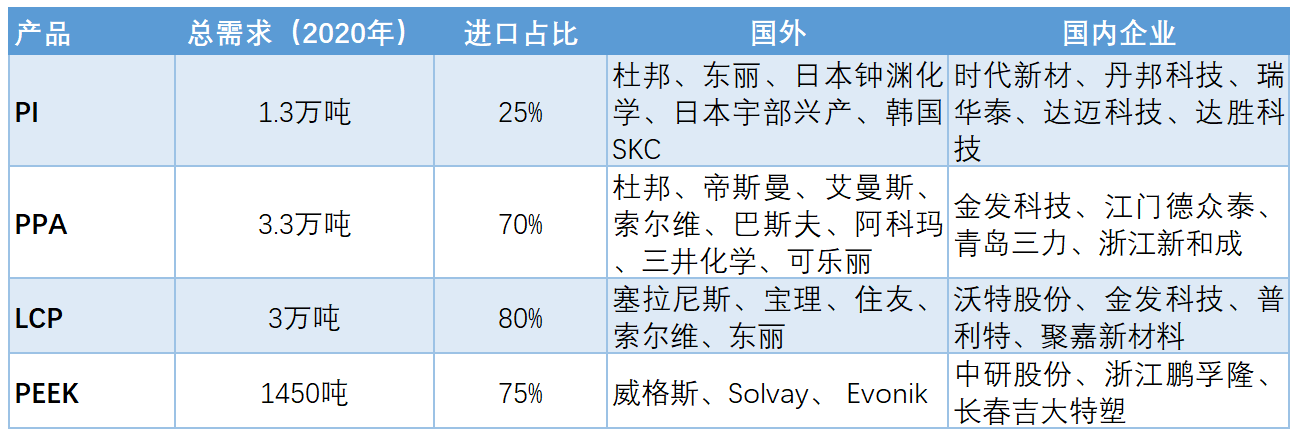
The development of special engineering plastics in China started in the mid-to-late 1990s. There is a huge gap compared with foreign leading enterprises, and the industry as a whole is still in the initial stage of development. Special engineering plastics belong to the leading industries of the national economy and are the key guarantee for high-end manufacturing. Their development in China has received great attention from the government and various scientific research institutions, and their strategic development status has been continuously enhanced. However, so far, it has not been possible to form a relatively large scale.
I. The Domestic Market of Special Engineering Plastics Products
01 | PI: The import dependence is approximately 25%, and the domestic PI films are gradually achieving the localization substitution of high-end products.
Polyimide (hereinafter referred to as PI) is an aromatic heterocyclic polymer compound containing an imide ring (-CO-NH-CO-) in the main molecular chain. It has excellent properties such as high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, high strength, high modulus, hydrolysis resistance, radiation resistance, corrosion resistance, high electrical insulation, and a low dielectric constant. It is listed as "one of the most promising engineering plastics in the 21st century".
Upstream: Dianhydride and diamine
Products: Films, fibers, composite materials, engineering plastics, foams, etc.
01 | PI: The import dependence is about 25%, and domestic PI films are gradually realizing the localization substitution of high-end products
Polyimide (hereinafter referred to as PI) is an aromatic heterocyclic polymer compound containing an imide ring (-CO-NH-CO-) in the main molecular chain. It has excellent properties such as high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, high strength, high modulus, hydrolysis resistance, radiation resistance, corrosion resistance, high electrical insulation, and a low dielectric constant. It is listed as "one of the most promising engineering plastics in the 21st century".
Upstream: Dianhydride and diamine
Products: Films, fibers, composite materials, engineering plastics, foams, etc.
PI film is the earliest PI product to achieve commercial application. With good performance, PI film is regarded as one of the three bottleneck key polymer materials for the development of high-tech industries in China. According to the application, PI films can be divided into electrical-grade PI films for the purpose of insulation and heat resistance, and electronic-grade PI films with performance requirements such as high flexibility and low coefficient of expansion.
Electronic-grade PI films are of high price and it is difficult for new entrants to enter the industry. Currently, it still belongs to an industry with high technical barriers and is known as the "golden film". 70% of the global production is concentrated in countries such as the United States, Japan, and South Korea. It is mainly monopolized by enterprises such as DuPont in the United States, Toray in Japan, Kaneka Corporation in Japan, Ube Industries in Japan, and SKC in South Korea. The production capacity is highly concentrated, and the scale of enterprises is mostly between 2,000 and 3,000 tons per year.
The PI film industry in China started late. Currently, there are about 70 PI film production enterprises in China, with the production capacity mostly around 100 tons, mainly applied in the low-end market. With the continuous increase in the demand for high-end electronic-grade PI films in China, domestic enterprises have begun to enter the high-performance PI film market.
At present, the enterprises with the production capacity of electronic-grade PI films above a certain scale in China include CRRC Times New Material Technology Co., Ltd., Danbang Technology Co., Ltd., Ru华泰 New Material Technology Co., Ltd., and Taiwan (China)'s Damai Technology Co., Ltd., Dasheng Technology Co., Ltd., etc. In 2019, the total production capacity of PI films in China reached 16,000 tons per year, with an operating rate of about 60%, and the output of high-end electronic-grade PI films was less than 1,000 tons.
From the perspective of demand, from 2016 to 2020, the compound growth rate of domestic demand for PI films was as high as 10%, and the total demand in 2020 was about 13,000 tons. Currently, the overall consumption of electronic-grade PI films and electrical-grade PI films in China is quite similar. In the future, with the rapid growth of electronic-grade application fields such as electronic display, flexible printed circuit (FPC), and thermally conductive graphite film, the consumption scale of electronic-grade PI films will further increase. It is expected that in 2023, it will exceed that of electrical-grade PI films. However, high-end electronic-grade PI films have high technical barriers in terms of equipment, process, and talents, and currently the development has entered a bottleneck period. In 2020, the import dependence of PI films in China was about 25%. With the accumulation of relevant R&D and technical talents in China, combined with the transfer of downstream key markets to the mainland market and the favorable relevant policies, the development of PI films in China will continue to accelerate, and gradually realize the localization substitution of high-end products.
02 | PPA: The import dependence is about 70%, and the domestic demand maintains a growth rate of over 8%
PPA has both the excellent properties of aromatic polyamides and the good molding and processing properties of aliphatic polyamides. After years of development, it has now become one of the main varieties of special engineering plastics and is widely used in fields such as electronics and electrical appliances, and the automotive industry. The electronics and automotive industries are the main consumer markets for PPA, accounting for more than 85% of the total consumption.
Upstream: Aliphatic diamines or diacids, aromatic diacids/diamines
Products: PA4T, PA6T, PA9T, PA10T, as well as PA11T and PA12T, etc.
Currently, the common PPA varieties in the market are mainly PA6T. Since the melting point of homopolymer PA6T exceeds its decomposition temperature, it is generally necessary to introduce a third monomer for copolymerization modification to reduce the melting point of the resin. Therefore, PA6T mainly exists in the form of copolymers, such as PA6T/66, PA6T/6I, etc.
According to statistics, the total production capacity of PPA resins abroad exceeds 150,000 tons per year, and the development is relatively mature. The main production enterprises include DuPont, DSM, EMS-GRIVORY, Solvay, BASF, Arkema, as well as Mitsui Chemicals in Japan and Kuraray. Among them, DSM, as a company that has mastered the industrialization solution of butanediamine globally, produces related products such as PA4T; Kuraray, with its unique technology of nonanediamine, was the producer of PA9T for a long time. With the expiration of Kuraray's PA9T patent, BASF has also gradually launched related PA9T products, while other foreign enterprises mainly produce PA6T products.
The industrialization of PPA in China started relatively late, and the global main production capacity and core production technologies are in the hands of foreign chemical giants. According to statistics, currently the total production capacity of PPA resins in China is about 16,000 tons per year. The main production enterprises include Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd., Jiangmen Dezhongtai New Material Co., Ltd., Qingdao Sanli New Material Co., Ltd., and Zhejiang NHU Co., Ltd. Among them, Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd. is a relatively large PPA resin production enterprise in China, mainly producing PA10T.
From the perspective of demand, from 2016 to 2020, the growth rate of domestic demand for PPA exceeded 10%, and the demand in 2020 reached 33,000 tons. However, due to the insufficient competitiveness of domestic PPA products, consumption still largely depends on imports, and the import dependence exceeds 70%. It is expected that in the next five years, the demand for PPA in China will maintain a growth rate of over 8%. By 2025, the domestic demand for PPA will reach 50,000 tons, and the rapid development of the electronics industry will still be the main driving force for the growth of PPA demand.
03 | LCP: The import dependence is about 80%, and the domestic consumption maintains a growth rate of over 6%
Liquid crystal polymer (hereinafter referred to as LCP) is an aromatic polyester material with a large number of rigid benzene ring structures in the main chain. It has the characteristics of low hygroscopicity, high temperature resistance, radiation resistance, hydrolysis resistance, weather resistance, corrosion resistance, natural flame retardancy, low coefficient of thermal expansion, high impact resistance, high stiffness, and vibration absorption performance.
Upstream: Aromatic polyesters, aromatic phenols, aromatic diacids
Products: Thermotropic liquid crystal TLCP, lyotropic liquid crystal LLCP
Currently, the global production capacity of liquid crystal polymers is about 78,000 tons per year, concentrated in the United States, Japan, and China. Among them, enterprises in the United States and Japan account for about 80% of the global total production capacity, and China accounts for only about 20%. The main overseas production enterprises include Celanese, Polyplastics, Sumitomo Chemical, Solvay, Toray, etc. Among them, Celanese and Polyplastics each account for more than half of the production capacity in the United States and Japan, and the industry concentration is relatively high.
China entered the LCP field relatively late. With the successive commissioning of multiple projects in recent years, the LCP production capacity has grown rapidly. By 2020, the domestic LCP production capacity reached 18,000 tons per year. The main production enterprises include Shenzhen沃特新材料股份有限公司 (Shenzhen Wotai New Material Co., Ltd.), Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd., Shanghai Precip Precision Materials Co., Ltd., and Zhejiang Jujia New Material Co., Ltd. Shenzhen Wotai New Material Co., Ltd. is a relatively large LCP production enterprise in China, with a total production capacity of 8,000 tons per year, accounting for about 45% of the national total production capacity.
From the perspective of demand, the domestic demand for LCP in 2020 was about 30,000 tons. Affected by technical and product quality factors, domestic consumption is highly dependent on imports, and the import dependence is about 80%. From the perspective of the consumption structure, electronics and electrical appliances are the main consumption fields of LCP, accounting for about 80% of the total consumption, mainly used for the production of connectors for various electronic devices. Currently, the total consumption in the 5G communication field is less than 1,000 tons. Driven by the "New Infrastructure Construction", it is expected that in the next five years, the consumption growth rate of LCP in the 5G communication field will reach more than 30%, and the consumption will reach 4,000 tons by 2025. Overall, it is expected that for some time in the future, driven by the demand in the electronics and electrical appliances and automotive fields, the total consumption of LCP will still maintain a growth rate of over 6%, and the total consumption will exceed 40,000 tons by 2025.
04 | PEEK: The import dependence is about 75%, and the domestic demand growth rate is as high as 15% - 20%
Polyetheretherketone (hereinafter referred to as PEEK) is a semi-crystalline, thermoplastic aromatic polymer material, and is the main variety in the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) series of polymers. It has flexibility and excellent processability.
Upstream: 4,4'-Difluorobenzophenone, Hydroquinone
Products: Films, fibers, coatings, carbon fiber composites, glass fiber composites
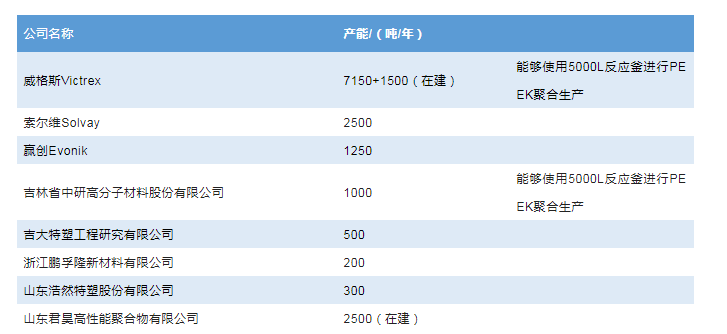
PEEK was initially developed by Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) in the UK in the late 1970s. Subsequently, its PEEK business was acquired by Victrex. Currently, Victrex is the largest PEEK producer globally, with a production capacity of about 7,000 tons per year, accounting for about 60% of the global total production capacity. The second and third largest producers globally are Solvay and Evonik respectively. Solvay's PEEK production capacity reaches 2,500 tons per year, mainly supplied for Apple mobile phones. Evonik's production capacity is about 1,250 tons per year, mainly exported to European countries and others.
The development of PEEK technology in China started relatively late. The representative R&D institution of the PEEK industry in China is Jilin University. The PEEK production capacity in China is mainly concentrated in Zhongyan Co., Ltd., Zhejiang Pengfulong New Material Co., Ltd., and Changchun Jida Tersu Co., Ltd., accounting for 80% of the total production capacity in China. Among them, the production capacity of Zhongyan Co., Ltd. reaches 1,000 tons per year, ranking first in the country. In the next five years, the PEEK production capacity in China will continue to expand. Currently, Victrex and Xingfu Chemical have announced the establishment of a joint venture in Panjin, and it is expected to build a PEEK production capacity of 1,500 tons per year.
From the perspective of demand, from 2016 to 2020, the growth rate of domestic demand for PEEK was as high as 20%. The demand in 2020 was approximately 1,450 tons, and the consumption of the product was mainly concentrated in the fields of electronics, automobiles, aerospace, and military industries.
On the one hand, the electronic information technology has developed rapidly in recent years. The development trend of integration and miniaturization of electronic components has brought opportunities for the consumption of PEEK resin. On the other hand, the excellent comprehensive properties of PEEK materials are in line with the lightweight requirements of the transportation industry. It is expected that in the next five years, the demand for PEEK in China will still maintain a growth rate of 15% to 20%, and the domestic demand for PEEK will reach approximately 3,000 tons by 2025.
II. Analysis of the Development Status
Currently, China has initially achieved the industrialization of varieties such as PI, PPA, LCP, and PEEK. Due to the relatively late start of research and development of special engineering plastics, there is a large gap compared with the advanced foreign level. The industry as a whole is still in the initial stage of development, and there are very few domestic enterprises with a say in the industry. This is mainly due to two reasons:
01 | The domestic accumulation of original technology is weak, and problems such as poor stability of product batches are common. Key core products are highly dependent on imports.
02 | The domestic downstream demand is relatively lagging, which restricts the development of the upstream material industry. The demand for high-end applications lags behind that of developed foreign countries.
III. Development Opportunities
From a policy perspective, special engineering plastics provide key guarantees for the development of the national economy, the upgrading of high-end manufacturing industries, and the construction of the national defense industry. They are key products in the national strategic emerging industries. To promote their industrialization process, the state has issued a series of favorable policies. The "Guidelines for the Development of the New Material Industry" regards engineering plastics as the focus of advanced basic materials, aiming to improve the international competitiveness of materials. Industrial policies such as the "Guiding Catalogue for the First Batch Application Demonstration of Key New Materials" and the "Classification of Strategic Emerging Industries" also continuously encourage the application and development of special engineering plastics.
From the perspective of demand, the global demand for special engineering plastics is steadily increasing year by year, especially the domestic market demand is growing rapidly, and the development prospects are promising. With the development of domestic industries such as new energy vehicles, 5G communication technology, and the "Two New and One Major" (new infrastructure construction, new urbanization construction, and major engineering construction such as transportation and water conservancy), it will inevitably drive the growth of demand for high-performance materials.



